The Aquarium Nitrogen Cycle
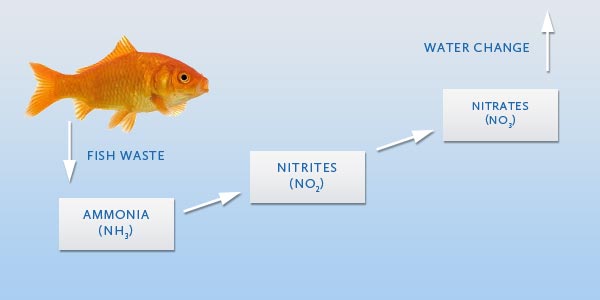
The cycle in which all decaying organic compounds such as fish waste, plant matter, excessive fish food, etc. breakdown is known as the Nitrogen Cycle. First decaying matter turns into Ammonia(NH3) which is toxic to fish at elevated levels. Second is Nitrite(NO2) and the third is Nitrate(NO3)
Nitrogen makes up about 78% of the earth's atmosphere. Despite this fact, there is very less usable nitrogen in the atmosphere because it is not biologically available and in many ecosystems there may actually be a nitrogen scarcity. Several biological and physical processes lead to nitrogen being converted to its different chemical forms which are actually usable.
This course of action is called The Nitrogen Cycle. There are many different processes involved in nitrogen cycle like fixation, mineralization, nitrification, and denitrification. From primary production to decomposition, all key ecosystem processes are affected by nitrogen availability. There are different chemical forms of nitrogen in which it is available in the environment like organic nitrogen, ammonium, nitrite, nitrate, nitrous oxide, nitric oxide or inorganic nitrogen gas.
Transforming nitrogen from one form to another becomes very vital. Microbes often carry out the processes for their own growth and to harvest energy. Even in oceans, the nitrogen cycle is a key process.
How to Cycle a New Aquarium
 There are multiple ways to cycle a newly established freshwater or saltwater aquarium, but the basic concept is to introduce some sort of organic matter to the tank so that it can decay and begin to produce bacteria.
The process of cycling an aquarium will take several weeks and all water should be dechlorinated before adding to the aquarium.
There are multiple ways to cycle a newly established freshwater or saltwater aquarium, but the basic concept is to introduce some sort of organic matter to the tank so that it can decay and begin to produce bacteria.
The process of cycling an aquarium will take several weeks and all water should be dechlorinated before adding to the aquarium.
Some of the ways to begin the nitrogen cycle include:
- Add A Fish: A small hardy fish will produce organic waste that will breakdown in the aquarium
- Fish Food: Add a small amount of fish food daily for a week
- Add Ammonia: This method is more for experienced aquarists as it can be easy to add too much. Make sure to use 100% ammonia that does not contain detergents or other cleaning agents
- Add Plants: Adding plants to a freshwater aquarium or macroalgae to a saltwater aquarium will not only introduce beneficial bacteria but will also consume nutrients from the water column
- Add Live Rock: Adding a few pieces of liverock to a saltwater aquarium will introduct beneficial bacterial as well as decaying matter
- Seed with Filter Media: Adding filter media from an established squarium will not only introduce bacteria to the aquarium but will also reduce the time needed for the aquarium to cycle
Regardless of which method you use to cycle your aquarium, the process is pretty much the same. Use an ammonia test to test the water each day. If the ammonia levels begin to exceed 1.0 then perform a 25-50% water change. Eventually the ammonia levels will begin to drop and the nitrite levels will begin to rise. Begin testing the nitrite levels daily until they begin to drop close to zero. After nitrite levels have dropped then you can begin to monitor the nitrate levels.
Do not being to stock your tank until the nitrate levels have stabilized. When you do being to add livestock to your aquarium, be sure to add it slowly. Do not heavily increase the bioload too quick or you could see a spike in nutrient levels.